Current trends in questionable online casinos have created a hostile environment for even the legitimate casino operators duly licensed by regulatory bodies. We’re sharing the very insightful article written by Wilson Chua who has looked into this matter in depth.
He not only is monitoring the issue over a prolonged period of time but is also gathering enough data to bring about proof of how urgent this matter is. More so now, even pages where government agencies and their services are also unknowingly or knowingly compromised as they take on advertisements to fund their department.
Read on and see how one can contribute to solving this issue and other ways Chua proposed to address this.
Malware Infected sites are seen as links at Gov.PH sites (Earlier article written on the 3rd of January 2023)
This is the backstory on the newer article for an update on how the situation has been addressed. This is the original list of gov.ph sites affected by questionable and malware-ridden sites.
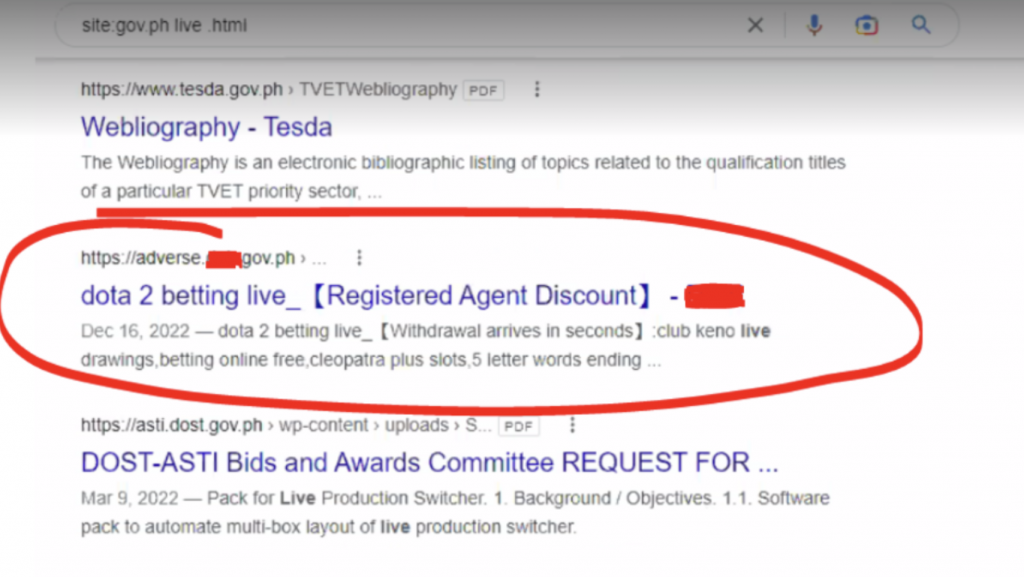
Here’s the thing. You did a Google search for some Gov.PH site information. But then, Google results could return search results with links like these below:
When searching for Gov.ph on Google results pop up you wouldn’t hesitate to click on it assuming that it’s a safe environment coming from an official site. But instead, you’re led to an online gambling environment.
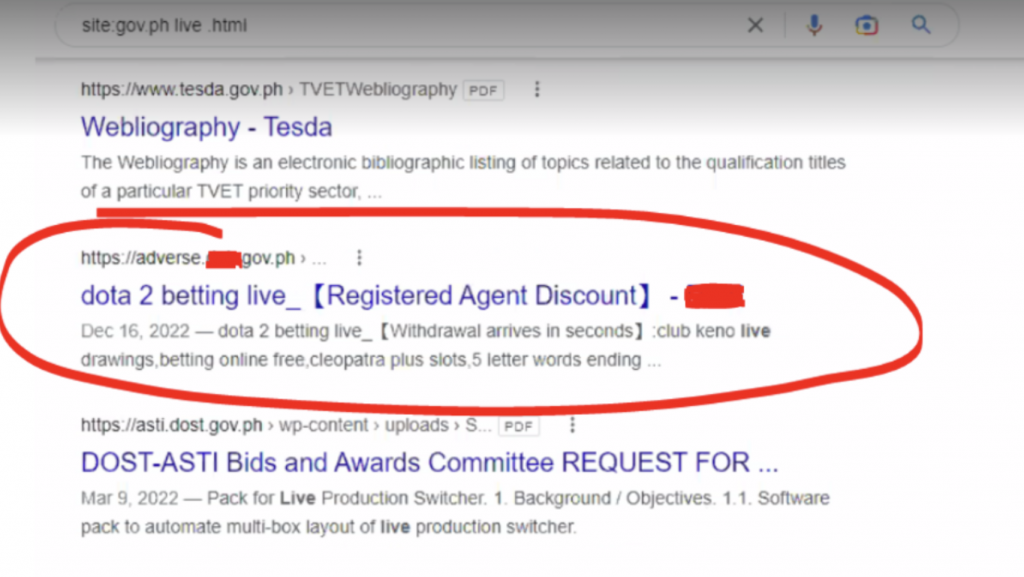
How did matters come to this?
Enter Eskie Maquilang who is a penetration testing engineer, KPMG first discovered this shocking tactic. Note: He did this in his personal capacity and as support to common friends.
Eskie noticed that hackers were triggering a lot of 403 errors (forbidden) on monitored servers. What got his attention were these URLs (uniform resource locators):
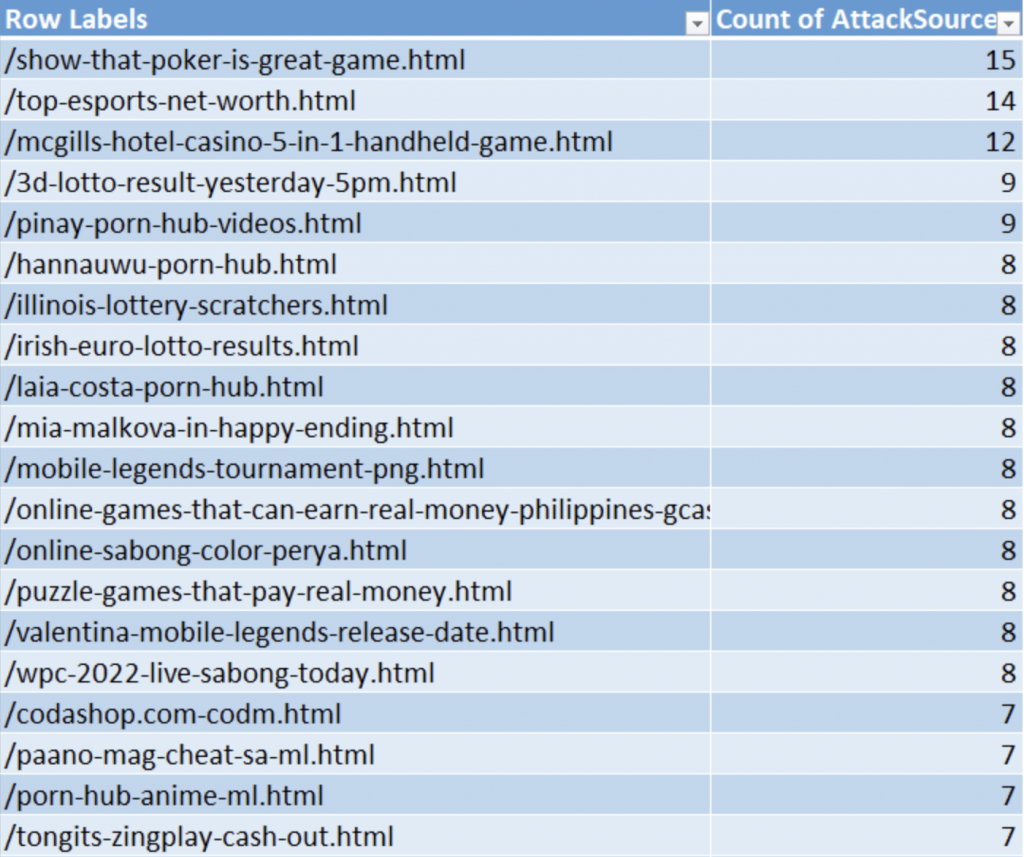
Why would these files be singled-out? Eskie believes that hackers are trying to confirm the presence of these files in your web server. If they are, this also means that your servers are already compromised.
They can easily upload the files via these vulnerable plug ins. Having the files in your webserver, Google spiders/bots will index them. Once in the index any search that matches it will be “served” by Google.
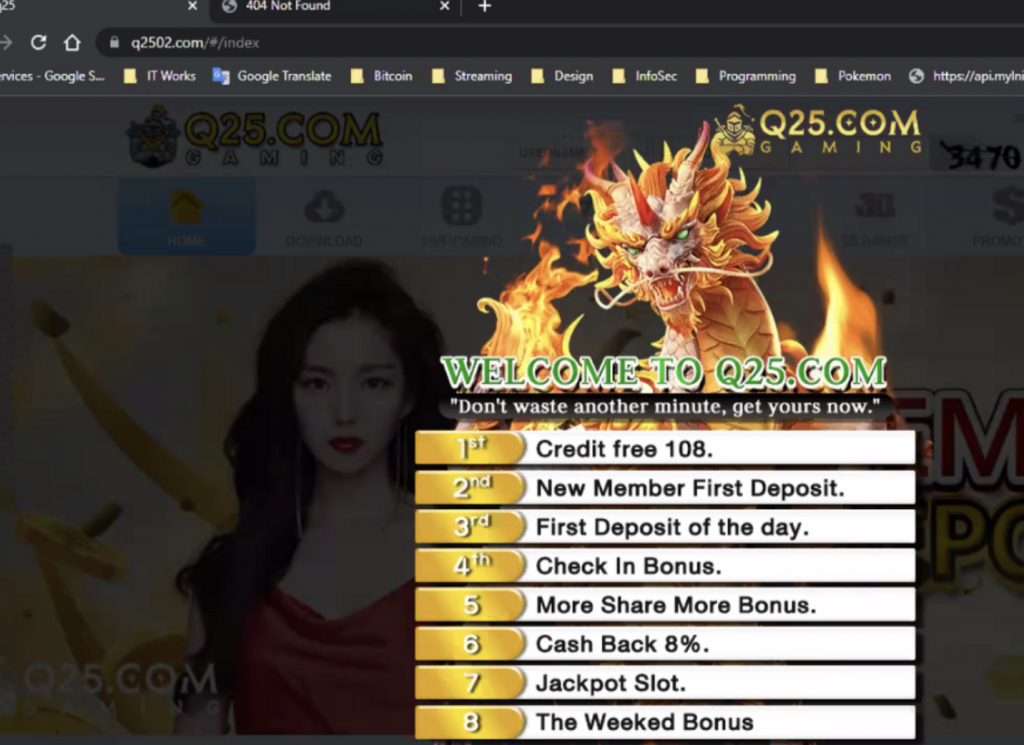
How would these files lead to gambling?
These files contain the code that redirects web visitors to the hackers’ preferred sites. It also checks on the referrer link. Doing this ensures that links ONLY work if the referee is from Google.com or Bing.com. Duck Duck Go is not affected, which is a good job for the company. The links WON”T work if you type it in directly, too.
How is this a dangerous matter?
This will lead into dangerous territory once the hackers decide to redirect web visitors to FAKE gov.ph sites, or to banking sites. Users can then be tricked into submitting confidential and sensitive information or by clicking on links deceptively trustworthy since the address is reflecting as gov.ph.
Once you click on the questionable link, malware is installed and ransomware will be thriving into your files. You’re now at the mercy of the hacker without even being aware of it.
What motivates them to do this?
Eskie thinks this is a “black hat” SEO (Search engine optimization) tactic. It aims to boost the rankings so these gambling sites show up higher in the Google Search engine results. Remember that links coming from Gov.ph sites are juicier in terms of SEO.
Black hat SEO practices are tactics that are used to manipulate search engine rankings in ways that violate the search engines’ terms of service. This is a form of spamming and is (supposedly) not allowed by search engines.
Is there a way to fix this?
- Use Google dork technics to see if your website is in the search results for such links. If your site comes up, better find those files and delete them.
- If you plan to pursue legal actions, it is best to get a screenshot of the file, including the creation time.
- You may want to report this incident to the Department of Information and Communications Technology (DICT) Cybercrime division. This can help to prevent others from falling victim to the same scam.
- Next, you MUST plug the ‘hole’ or the vulnerability that was used to get the files there in the first place. Some of the steps you can take to fix this file upload vulnerability in WordPress:
- Update WordPress to the latest version: WordPress regularly releases updates that include security fixes. Make sure that you are running the latest version of WordPress to protect against known vulnerabilities.
- Install a security plugin: There are many security plugins available for WordPress that can help protect against file upload vulnerabilities.
- Some popular options include Wordfence and Sucuri Security. These plugins can help to block malicious file uploads and alert you if any suspicious activity is detected on your site.
- Use strict file upload validation: When allowing users to upload files to your WordPress site, make sure to validate the files to ensure that they are safe. This can be done by checking the file type, size, and content of the uploaded file. You can use WordPress functions like wp_check_filetype() and wp_check_file_size() to do this.
- Use a dedicated file upload folder: Instead of allowing users to upload files to any location on your site, create a dedicated folder for file uploads. This will help to prevent users from uploading malicious files to important areas of your site.
- Use a secure hosting provider: Your hosting provider plays a key role in the security of your WordPress site. Make sure to choose a hosting provider that has strong security measures in place to protect against file upload vulnerabilities and other types of attacks.
- Finally, please enable WAF! (Web Application Firewall). WAF automatically screens web requests and filters out likely attacks on your webserver. As always, I love hearing from you, do share your insights on this.
Links that have been fixed
Links that still directs users to Gambling and Casino sites
Why are these malware links still working?
Government agencies, like any organization, may experience delays in addressing vulnerabilities for a variety of reasons. Some of the most common include:
Limited resources: Government agencies often have limited budgets and staff, which can make it difficult to allocate resources towards addressing vulnerabilities.
This can be especially true for smaller agencies or those that have other pressing priorities. (Idea from: https://www.prominentfc.com/business-services-faq/)
Bureaucracy: Government agencies are often subject to bureaucratic processes and regulations that can slow down decision-making and action. For example, there may be multiple levels of approval required before a vulnerability can be fixed, or certain procedures that must be followed before taking action.
Complex systems: Government agencies often have complex systems in place, such as legacy systems or systems that are critical to the functioning of the agency. Fixing vulnerabilities in these systems can be more difficult and time-consuming than in simpler systems.
Risk management: Government agencies may prioritize addressing vulnerabilities based on the level of risk they pose. High-risk vulnerabilities may be addressed quickly, while low-risk vulnerabilities may be given a lower priority. (Idea from: https://www.strobes.co/blog/the-top-10-vulnerabilities-of-2022-mastering-vulnerability-management)
Lack of expertise: Government agencies may lack the internal expertise to address certain vulnerabilities, which can slow down the process of identifying and fixing them.
Collaboration: Government Agencies may need to collaborate with other agencies or organizations to address vulnerabilities, which can slow down the process as coordination and communication are needed.
What Government must do
There are several steps that government agencies can take to resolve malware links faster:
- Implementing automated systems: Automated systems, such as intrusion detection and prevention systems, can quickly identify and block malware before it can cause damage.
- Regularly update software and systems: Regularly updating software and systems can help ensure that vulnerabilities are patched in a timely manner, which can reduce the risk of malware infections.
- Providing employee education and training: Employee education and training can help reduce the risk of malware infections by ensuring that employees are aware of the risks and know how to identify and avoid malicious links.
- Creating incident response plans: Having a well-defined incident response plan in place can help ensure that the agency can respond quickly and effectively to malware incidents.
- Enhancing internal security measures: By implementing internal security measures, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and antivirus software, government agencies can help protect against malware and other cyber threats.
- Sharing threat intelligence: By sharing threat intelligence with other government agencies and organizations, government agencies can help identify and respond to malware threats more quickly.
- Collaborating with Cybersecurity vendors: Government agencies can work with DICT’s cybersecurity teams to ensure that their systems and networks are protected against known and emerging threats.
- Outsource to a managed security service provider, the tedious tasks of monitoring their logs and networks for malware and other threats.
- Conducting regular security assessments: Government agencies can conduct regular security assessments to identify vulnerabilities and risks in their systems and infrastructure, which can help them address malware threats more quickly.
It’s worth noting that while these are steps that can be taken to improve the response time to malware links, it’s important to have a comprehensive security strategy that includes preventative, detective, and corrective measures to protect against cyber-attacks.
Chua also thanked SecOPs interns from the University of Pangasinan for helping to do the verification tasks on each of these sites. The list of malware links came from Eskie Maquilang, penetration testing engineer, at KPMG.
Wrapping things up
Squelching these abominable acts certainly need everyone’s contribution to stop this from happening. It’s best to be highly aware of one’s activities online and it sure helps to think before you click on anything. We hope that Chua’s article was a great help. It certainly made us sharper in discerning the good practices we need to follow to avoid being hacked.
Let us know if you would like to see more articles about this, too. Just comment in the section below. We’ll get the topics you’re interested in readily available on our pages. Stay safe everyone and cheers!